DynamoDB Sort Key - The Ultimate Guide [w/ Code Examples]

Written by Andrea Perera
Published on March 21st, 2022
Time to 10x your DynamoDB productivity with Dynobase [learn more]
What is Sort Key in DynamoDB
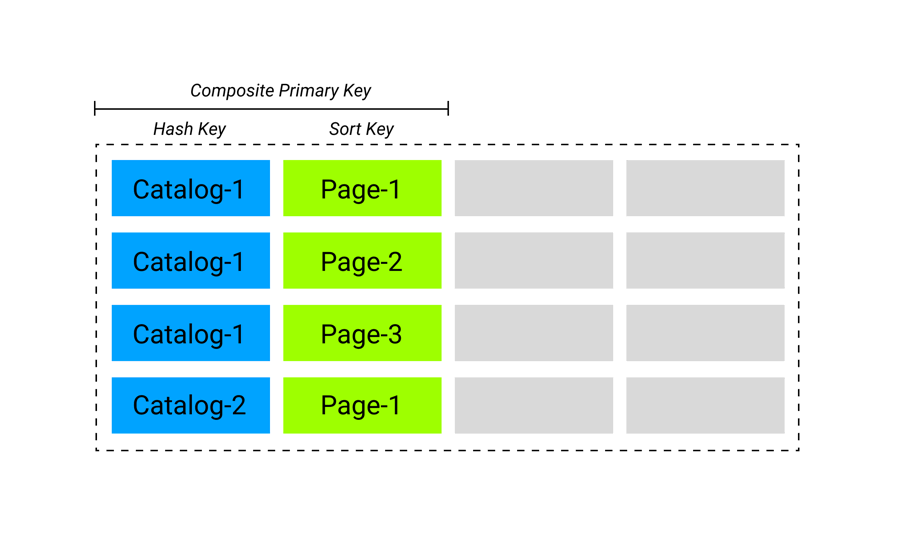
DynamoDB supports two primary keys: the partition key and the composite primary key. The partition key is a single attribute, whereas the composite primary key is a combination of two attributes named the partition key (also known as the hash key) and the sort key (also known as the range key).
The sort key is also known as a range attribute of an item, and it helps to organize related information in a single location where it can be efficiently queried. This allows for more complex queries and better data organization within a partition.
Sort Key vs. Other Key Types
Sort Key vs. Partition Key
DynamoDB uses the partition key as an input to the hash function. The hash function's output decides which partition the item will be placed in, and all items with the same partition key value are stored together.
The sort key is used to sort and order items within a partition. Multiple items with the same partition key value are feasible, but they must have different sort key values. This means you can have multiple items with the same partition key, but the sort key must be unique within that partition.
Sort Key vs. Range Key
An item's sort key is also called its range attribute. The range attribute refers to how DynamoDB stores items with the same partition key physically close together, sorted by sort key value. This allows for efficient querying of items within the same partition.
Working with Sort Key (Code Examples)
How to Add a Sort Key
First, let's create an object called Book which represents an item in a DynamoDB table. The Book class is accessible via getter and setter methods to correctly persist the data using DynamoDBMapper.
In this example, the primary key for Book is made up of two attributes: BookAuthor (partition key) and BookTitle (sort key). You can query data using the partition key or the composite primary key.
However, you need to add the sort key at the initial table creation stage as you cannot add a sort key to an already existing table.
How to Change a Sort Key
You cannot change the sort key after the table is provisioned. If you need to change the sort key, you must create a new table, migrate the existing data to the newly created table, and then delete the old table.
Query by Sort Key
To query by sort key, you need to use both the sort key and the partition key. The query is quicker and cheaper than a scan, and you can fetch up to 1MB of records. The following code shows how to query by the sort key in Java.
Query by Sort Key Only
You cannot query only using a sort key. You need to specify a partition key to perform query operations. Alternatively, you can create a global secondary index or perform a scan operation.
Query with Sort Key Filter
The following Java code example retrieves only "Science Fiction & Fantasy" types of books written by J. K. Rowling, with book titles (sort key) that begin with the letter "H" through the letter "S."
Query Sort Key Descending
The sort key value is always used to sort query results. If the sort key is a number, the results will be returned in numerical order. Otherwise, the results will be returned in UTF-8 bytes order. The sort order is set to ascending by default. However, you can set the ScanIndexForward parameter to false if you need the sort order to be descending.
Best Practices For Using Sort Keys in DynamoDB
- You cannot change the sort key after the table is provisioned. Therefore, be mindful when creating a sort key.
- If your data contains hierarchical (one-to-many) relationships and you want to query at any hierarchy level, use a composite primary key. For example, an address that contains zip code, postal code, country, city, etc.
- The sort key should be structured as follows:
- You can use the sort key along with a prefix to keep a record of item-level revisions such as V0, V1, V2, etc.
- If you need to query a subset of items, use a composite primary key. For example, if you only provide the value for the
BookAuthor, DynamoDB retrieves all of that author's books. You can provide a value for theBookAuthorand a range ofBookTitlevalues to retrieve only a subset of books by a specific author. - Sort key only supports string, number, or binary data types.
- Always try to use a composite primary key as the primary key. If you only use the partition key as the primary key when creating a table, you won't be able to perform query operations or use key condition expressions.
Global Secondary Indexes (GSIs) and Local Secondary Indexes (LSIs)
In addition to the primary key, DynamoDB allows the creation of secondary indexes to enable more flexible querying. A Global Secondary Index (GSI) can have a different partition key and sort key from the base table, allowing for more complex queries across different attributes. A Local Secondary Index (LSI), on the other hand, uses the same partition key as the base table but allows for a different sort key. These indexes can significantly enhance query capabilities and performance, especially for read-heavy applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can we update the sort key in DynamoDB?
No, you cannot update the sort key after the table is provisioned. However, you can create a new table, migrate the existing data to the newly created table, and delete the old table.
2. Can we query DynamoDB without a sort key?
Yes, you can use the partition key value of the item to query data.
3. Is a sort key required in DynamoDB?
No, but having a sort key will improve query efficiency and flexibility.
4. How many sort keys can DynamoDB have?
There should only be one sort key defined per table. However, it can be composed using multiple columns.